The term bot, derived from “ro-bot” in its generic form. It is a script or set of scripts or a computer program
which is designed to perform predefined functions repeatedly and
automatically after being triggered intentionally or through a system
infection. Bot runs automated tasks over internet. According to the type
of working we can say that there are two of Bots.
Benevolent bots: Bots that are used to carry out legitimate activities in an automated manner are called benevolent bots. These are used in search engines to spider online website content and by online games to provide virtual opponent.
Malicious bots: Bots that are meant for malicious intent are known as malicious bots. bots used for DDos attack and spam bots are example of Malicious bots.
The first bot program Eggdrop created by Jeff Fisher in 1993 originated as a useful feature on Internet Relay Chat (IRC) for text based conferencing on many machines in a distributed fashion.
An IRC malicious bot program runs on an IRC host or client each time it boots in a hidden manner and controlled by commands given by other IRC bot(s). It is typically an executable file with a size of less than 15 KB in its compressed form. An IRC host computer running an IRC bot malware program becomes a Zombie or a drone (Choo – 2007).
The first malicious IRC bot, Pretty Park Worm that appeared in 1999 contained a limited set of functionality and features, such as the ability to connect to a remote IRC server, retrieve basic system information e.g. operating system version, login names, email addresses, etc.
A collection of such type of bot affected systems are know as BOTNET (Bot Networks). A collection of compromised hosts or bot-infected machines running malware such as worms, Trojan horses, or backdoors under command & control (C&C) infrastructure.
Benevolent bots: Bots that are used to carry out legitimate activities in an automated manner are called benevolent bots. These are used in search engines to spider online website content and by online games to provide virtual opponent.
Malicious bots: Bots that are meant for malicious intent are known as malicious bots. bots used for DDos attack and spam bots are example of Malicious bots.
The first bot program Eggdrop created by Jeff Fisher in 1993 originated as a useful feature on Internet Relay Chat (IRC) for text based conferencing on many machines in a distributed fashion.
An IRC malicious bot program runs on an IRC host or client each time it boots in a hidden manner and controlled by commands given by other IRC bot(s). It is typically an executable file with a size of less than 15 KB in its compressed form. An IRC host computer running an IRC bot malware program becomes a Zombie or a drone (Choo – 2007).
The first malicious IRC bot, Pretty Park Worm that appeared in 1999 contained a limited set of functionality and features, such as the ability to connect to a remote IRC server, retrieve basic system information e.g. operating system version, login names, email addresses, etc.
A collection of such type of bot affected systems are know as BOTNET (Bot Networks). A collection of compromised hosts or bot-infected machines running malware such as worms, Trojan horses, or backdoors under command & control (C&C) infrastructure.
Types of Botnets: There
are a variety of botnets in existence today. The three most commonly
seen on home and office client computers are HTTP botnets that exploit
vulnerabilities in web browsers, IRC botnets that allow operators to
control the computers of unsuspecting users through an internet relay
chat (IRC) channel, and Peer to Peer (P2P) botnets that infect files shared on P2P services like Gnutella or Limewire.
HTTP Botnets:HTTP
typically is used for creation and control of botnets. Bots will sign
in to an http server and wait for commands from a bot herder, or they
will simply visit pre-designated sites to get commands that are coded
into the site’s files. Many HTTP bots have their own servers for
downloading malware, phishing, etc.
P2P Botnets:Many
P2P applications are utilized by bot herders to share files that have
bots and malware attached. In most cases, these bots are pre-programmed
to perform specific functions when a file is opened, or when a container
application like a game or desktop application is installed.
IRC Botnets: The
most abundant use of botnets is accomplished using IRC applications.
This is because the IRC protocol has been around the longest, and that
is where earlier botnets operated before HTTP came along. IRC is used by
a wide variety of applications to allow users to have simple text based
chatting environments. Infected IRC clients log into a specific IRC
server and wait for specially formatted text messages that contain
commands. Commands can also be encoded into the title or name of the
chat channel, so that every bot entering can be given commands. More
sophisticated versions of this will group bots into sub-nets based on
the tasks to be performed, or some other distinction. IRC Botnets are
generally the most complex and the hardest to detect.
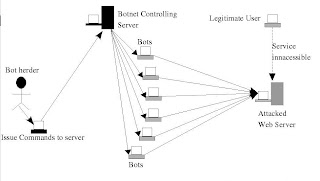
this
is the diagram which shows how an attacker spread his bots on victims
computer and control those bot program. Mostly these Affected systems
are use for illegal activities by attacker without the knowledge of
system owner.
Look at the figure which shows how botnets are used in DDos attacks.
How to Avoid Botnets:
- Install an antivirus program from a trusted provider.
- Make sure the operating system’s firewall is turned on, as well as the firewall of any connected router(s).
- Keep your operating system, web browser, firewall and antivirus applications up to date.
- Keep all media players up to date.
- Pay close attention to the options available when installing downloaded software. Installing toolbars or other gadgets that come from sources other than the site they were created on may have bots attached to the install. Also be skeptical of installation options that ask for permission to change your browser’s home page.
- Learn to be very critical of emails containing links of any kind or ask you to go to a specific site that you’re unfamiliar with.
if you have any query regarding this post please comment.

No comments:
Post a Comment